

They run from an anterior origin to meet posteriorly in the midsagittal plane, forming a. Patients with oropharyngeal carcinoma (OPC) often have difficulty swallowing, which may affect quality of life (QoL). There are three circular pharyngeal constrictor muscles the superior, middle, and inferior pharyngeal constrictors. These results provide information that will help a comprehensive understanding of the effects of pharyngeal muscles on movement. The pharyngeal constrictor muscles encircle the pharynx and larynx.
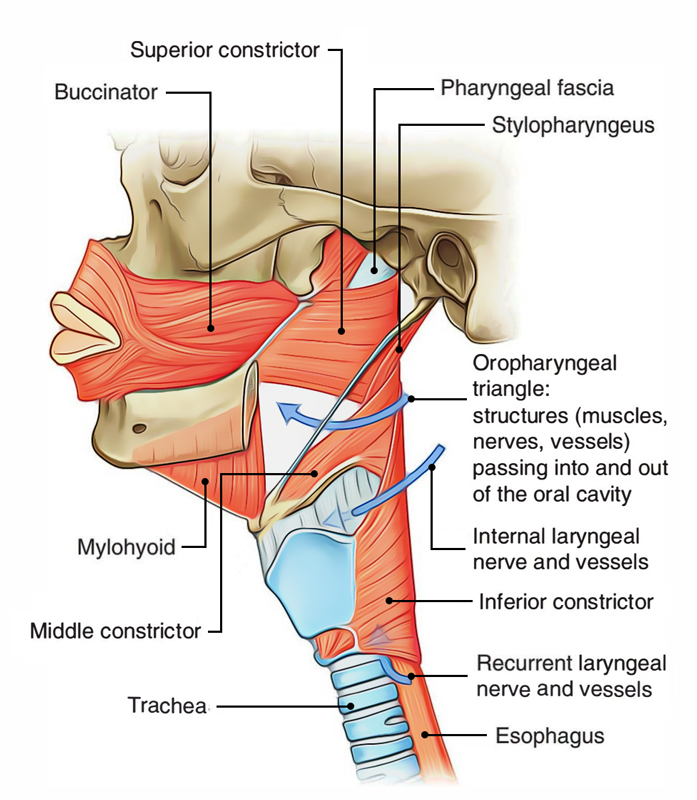
The variant muscle bundles play their own role in pharyngeal movement according to their morphology. The mostcaudal portion of the IPC is believed. What elevates the larynx Inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscles : attaches anteriorly along the lateral regions of the thyroid and cricoid cartilages, and runs superiorly and posteriorly to meet with opposing fibers. A variation of the STP, in which it ran transversely and merged with the SC muscle, was found in 2.3% (1/44) of cases while a variation of the SC muscle, in which it ran longitudinally and merged with the contralateral constrictors, was found in 11.4% (5/44). The posterior wall of the airway is largely comprised of the pharyngeal constrictor muscles which wrap around the airway and so also contribute to the lateral. The inferior pharyngeal constrictor (IPC) muscle functions during swallowing, respiration, and vocalization. The superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle is innervated by the pharyngeal branch of the vagus nerve via the pharyngeal plexus. The middle pharyngeal constrictor attaches to the greater horn of the hyoid bone and contributes to the pharyngeal stripping wave 12 (Figure 1). It is the highest positioned muscle among the three pharyngeal constrictors.

The accessory bundle of STP and petropharyngeus was found in 18.2% (8/44) and 25.0% (11/44) of cases, respectively. The superior pharyngeal constrictor attaches anteroinferiorly at the alveolar process of the mandible and collapses toward the tongue base during swallowing. The superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle is a muscle in the pharynx. Forty-four specimens (22 right and 22 left sides) from embalmed Korean adult cadavers (13 males, 9 females age range, 46–89 years mean age, 69.2 years) were used in this study. They are innervated by the pharyngeal branch of the vagus nerve (CN X) with the exception of the stylopharyngeus muscle which is innervated by the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX).The aims of this study were to clarify the topography and variations stylopharyngeus (STP) and superior constrictor (SC) muscles, and to examine what role they play in the pharyngeal movement. There are two muscular layers of the pharynx: the outer circular layer and the inner longitudinal layer.ĭuring swallowing, these muscles constrict to propel a bolus downwards (an involuntary process).ĭuring swallowing, these muscles act to shorten and widen the pharynx. and middle pharyngeal constrictor muscles as well as the glottic and supraglottic larynx appear to be the most critical OAR, and reducing their radiation. The pharyngeal muscles (involuntary skeletal) push food into the esophagus. The pharyngeal muscles are a group of muscles that form the pharynx, which is posterior to the oral cavity, determining the shape of its lumen, and affecting its sound properties as the primary resonating cavity.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
